Suction pump use conditions and classification
Suction pump refers to the downhole device driven by the pumping engine to lift the crude oil in the well to the surface.
Ordinary pumping pump is mainly composed of four parts: pump barrel, suction valve, piston and removal valve. Suction pump refers to the downhole device driven by the pumping engine to lift the crude oil in the well to the surface.
Ordinary pumping pump is mainly composed of four parts: pump barrel, suction valve, piston, and removal valve. According to the pumping pump in the well fixed way, can be divided into tube pumps and rod pumps.
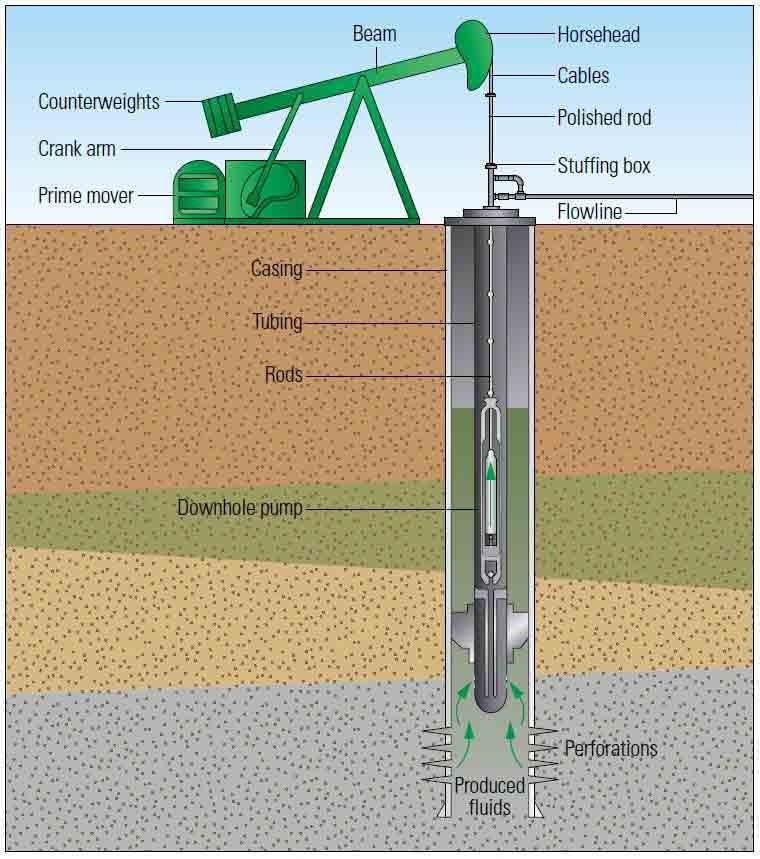
Suction pump is the downhole equipment for pumping oil. The liquid it draws contains sand, wax, water, gas and corrosive substances, and it works downhole in hundreds to thousands of meters, and the pressure inside the pump may be as high as 10MPa or more.
Therefore, its working environment is complex, harsh conditions, and the pump’s performance directly affects the well yield. Therefore, pumping pumps should generally meet the following requirements: (1) simple structure, high strength, and high efficiency.
(1) simple structure, high strength, good quality, reliable sealing of connecting parts.
(2) Manufacturing materials are wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant, and have a long service life; (3) The specifications can meet the requirements of oil well production.
(3) specifications to meet the needs of the oil well discharge volume, adaptability.
(4) It is easy to lift up and down.
(5) The structure should be considered sand-proof, gas-proof, and with the necessary auxiliary equipment.
Classification:
Tubular pumps: Tubular pumps, also known as tubular pumps, are characterized by assembling the outer barrel, liner and suction valve on the ground and connecting them to the lower part of the tubing to be lowered into the well first, and then the piston equipped with the discharge valve is lowered into the pump through the tubing by means of the pumping rod.
The liner is machined from material into several sections and lined inside the outer barrel.
Piston is made of seamless steel pipe hollow cylinder, smooth outer surface with annular grooves, the role of the piston and liner into the gap between the sand gathered in the grooves, to prevent sand abrasion of the piston and the liner, and grooves in the oil stored in the lubrication of the role of the piston surface.
Inspection of the pump to drain off the oil in the oil pipe when starting the pump, can be used to salvage the suction valve (fixed valve), by lowering the rod column, so that the lower end of the piston buckle bite the suction valve salvage head, the suction valve to put forward.
However, this kind of pump, due to the salvage head of the suction valve occupies the space inside the pump, so that the pump’s anti-punching distance and the residual clearance volume is large, and it is easy to be affected by the gas and reduce the pumping efficiency.
Most wells with tubular pumps are installed with oil drain in the lower part of the tubing, and the oil in the tubing is unloaded by opening the drain.
In the well into the big pump, due to the piston diameter is larger than the inner diameter of the tubing, can not be through the tubing into the piston, the method used is the first piston with the tubing into the well, and then into the pumping rod column, the use of a device known as a decoupler and the pump piston docking.
Tubular pump structure is simple, low cost, in the same diameter of the tubing allows the pumping diameter under the rod pump is larger, thus the displacement is large.
However, when checking the pump must be up and down the tubing, repair workload, so it is suitable for under the pump depth is not large, high yield wells.
Rod pump: rod pumping pump also known as the insertion of the pump, which is characterized by a fixed cylinder top fixed rod pump is inside and outside the two barrels, the upper end of the outer barrel is equipped with a vertebrae seat and the spring (the location of the spring for the depth of the pump), the pump down the outer barrel with the tubing first into the well, and then fitted with a liner, the inner barrel of the piston is connected to the pumping rod at the lower end of the barrel down to the outer working tube and fixed by the spring.
In addition, there is a fixed point at the bottom of the pump barrel fixed barrel bottom fixed rod pump, and the piston is fixed at the bottom, driven by the pumping rod pump barrel up and down reciprocating motion of the dynamic barrel bottom fixed rod pump.
When checking the pump, there is no need to take up the oil pipe, but through the pumping rod to pull out the inner working cylinder.
Rod pump check pump convenient, but the structure is complex, high manufacturing cost, in the same diameter of the tubing allows the pump diameter into the teaching tube pump to be smaller, suitable for pumping a greater depth, the yield of smaller oil wells.

Conventional pumping pumps exist metal piston and liner processing requirements, manufacturing inconvenience, and easy to wear the shortcomings.
Downhole View of sucker rod pump/downhole pump/tubing pump/API11AX – YouTube

 By Sun
By Sun

